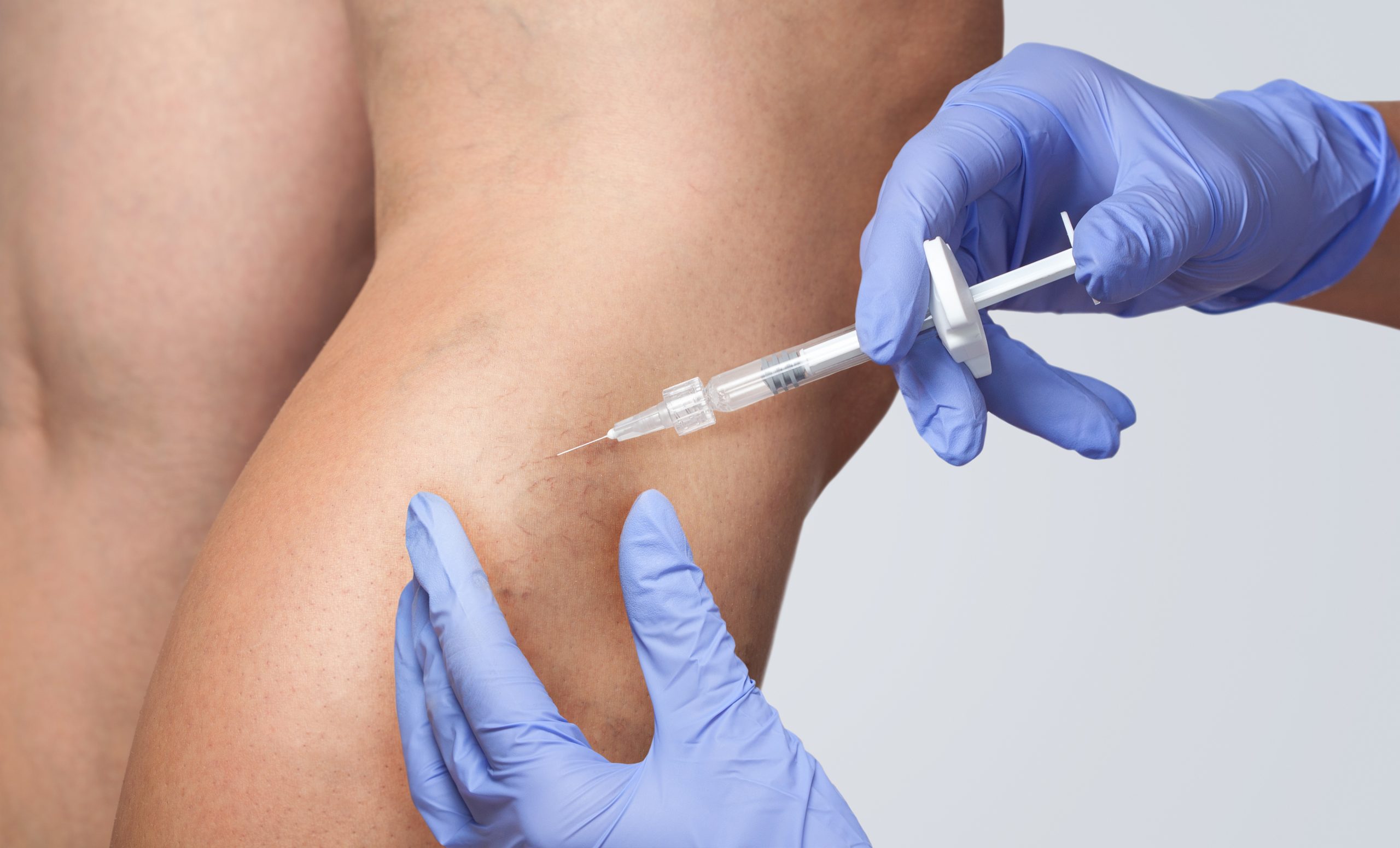
One option for patients who have issues related to varicose or spider veins is a treatment known as sclerotherapy.
Varicose veins are essentially just bulging veins that have become incompetent. The way sclerotherapy works is by injecting a solution into the veins. The solution irritates the lining of the blood vessel and causes it to collapse.
Typically in sclerotherapy, the solution used is a hypertonic saline solution. While effective, the saline solution does have some drawbacks.
Drawbacks of Saline
Some patients express feeling some discomfort or stinging sensations when a hypertonic saline solution is used. Patients may also experience cramping during the process, and that cramping can be uncomfortable for patients.
Another drawback to the hypertonic saline solution is that it can cause some short-term or even lasting staining in the legs where the collapsed veins are. Obviously, for patients who are seeking treatment for varicose veins due to aesthetic issues, staining is an issue that causes concern for them.
Advantages of Asclera
Another option for sclerotherapy is Asclera. Asclera is a detergent solution that works in the same way as the hypertonic saline solution.
While Asclera is a higher-priced option than traditional hypertonic saline, Asclera carries some advantages that patients find are worth the extra cost.
For instance, Asclera does not cause any stinging sensations. Patients using Asclera have not reported any discomfort from cramping, either.
Also, Asclera leaves little to no staining, and for those patients who are concerned about the aesthetics of treating varicose veins, this can prove to be a very important issue.
Asclera may not be the right choice for all patients, but to avoid the issues related to using hypertonic saline solutions, it is definitely an option worth considering.
Consult With Your Physician About Sclerotherapy
Asclera is a premium product, and patients seeking treatment for varicose veins should consult their care provider to determine which route will be the best for them.